To deliver a comprehensive, comparative analysis of cancer care systems across 42 diverse countries, with a strong focus on five of the most burdensome cancers globally, breast, lung, colorectal, prostate, and gastric. This study applies a unified 7-pillar maturity index to assess how health systems perform in areas such as infrastructure, access to diagnostics and treatment, clinical practices, and financial protection. While drawing lessons from a wide range of health system models, this presentation puts a spotlight on the Focus countries. The aim is to leverage global benchmarks to identify opportunities for reform, innovation, and improved equity in the cancer care continuum.
Compare cancer care maturity across 43 countries using standardized maturity scores, identifying global trends, strengths, and systemic gaps to guide international alignment with best practices.
Apply a unified maturity framework to assess performance in infrastructure, treatment access, survival outcomes, biomarker utilization, clinical guidelines, reimbursement systems, and screening programs, enabling robust cross-country and regional comparisons
Examine challenges and successes in comparable health systems across regions to extract feasible, context-sensitive strategies applicable to diverse settings.
Engage policymakers, healthcare leaders, and patient advocates to co-develop targeted policy and program priorities, leveraging real-world data and global best practices for impactful cancer care improvement.
 Infrastructure
Infrastructure
| Measure | Scale |
|---|---|
| Specialized Cancer Centers | 1-5 |
| Genetic & Molecular Testing Infrastructure | 1-5 |
 Treatment Access, Research Funding & Awareness
Treatment Access, Research Funding & Awareness
| Measure | Scale |
|---|---|
| Treatment Access | 1-5 |
| Research Funding | 1-5 |
| Awareness Campaigns | 1-5 |
 Survival, Early Detection & Palliative Care
Survival, Early Detection & Palliative Care
| Measure | Scale |
|---|---|
| Survival Rates | 1-5 |
| Early Detection | 1-5 |
| Palliative Care | 1-5 |
 Biomarker Utilization
Biomarker Utilization
| Measure | Scale |
|---|---|
| HER2 | % Coverage |
| Estrogen Receptor (ER) | % Coverage |
| Progesterone Receptor (PR) | % Coverage |
| BRCA1 | % Coverage |
| BRCA2 | % Coverage |
 Clinical Guidelines
Clinical Guidelines
| Measure | Scale |
|---|---|
| National Guideline Implementation | 1-5 |
| Feasibility of Integration | 1-5 |
| Adoption of International Guidelines | 1-5 |
| Engagement with Updates | 1-5 |
| ESMO Guidelines Implementation | 1-5 |
 Reimbursement Systems
Reimbursement Systems
| Measure | Scale |
|---|---|
| Reimbursement | 1-3 |
| No-Cost Access | 1-3 |
| Measure | Scale |
|---|---|
| Type of Screening Program | Descriptive |
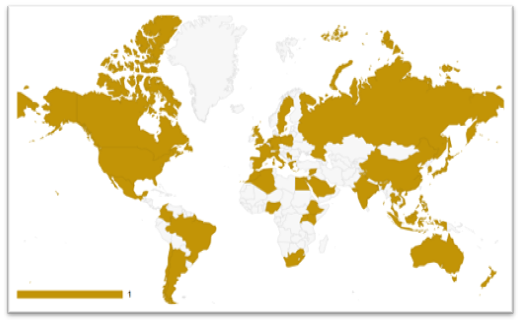
| North America | Europe | Asia | Africa | Latin America & Caribbean | Oceania |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | United Kingdom | Japan | South Africa | Mexico | Australia |
| Canada | Germany | South Korea | Kenya | Brazil | New Zealand |
| France | China | Nigeria | Argentina | ||
| Netherland | India | Egypt | Chile | ||
| Sweden | Singapore | Morocco | Colombia | ||
| Italy | Thailand | Algeria | |||
| Spain | Saudi Arabia | Ethiopia | |||
| Poland | UAE | Rwanda | |||
| Greecs | Syria | Uganda | |||
| Russia | Indonesia | ||||
| Serbia | Vietnam | ||||
| Philippines | |||||
| Malaysia |
| Pillar | Level 1 (Critical) - Least Developed | Level 2 (Emerging) - Underdeveloped | Level 3 (Intermediate) - Developing | Level 4 (Advanced) - Well Developed | Level 5 (Leading) - Highly Developed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | No specialized cancer infrastructure; basic hospitals lack diagnostic or oncology units. | Select tertiary hospitals offer basic cancer services; most regions underserved. | Moderate access in regional centers; basic pathology, imaging, and oncology units exist. | Well-distributed cancer centers with full diagnostics and treatment capabilities. | Nationwide network of specialized cancer institutes with digital and AI-enabled systems. |
| Treatment Access, Research Funding, and Awareness Campaigns | Only generic chemotherapy is available; no clinical trials or awareness initiatives. | Some chemotherapy options; few research grants, limited campaigns. | Public access to chemotherapy and some targeted therapies; national research budgets growing. | Widespread access to modern treatments; robust national research and funded awareness campaigns. | Cutting-edge treatments (immunotherapy, research pipeline, high-profile national campaigns). |
| Survival Rates, Early Detection, and Palliative Care | Survival <10%, late-stage diagnosis is the norm; palliative care absent. | Survival 10-20%, early detection rare; some hospitals offer pain management. | Survival 20-35%, early detection phase; regional palliative services exist. | Survival 35-50%; structured early detection and nationwide palliative care programs. | Survival >50% population-based early detection, full palliative and survivorship programs integrated. |
| Utilization of Biomarkers | No biomarker testing; no labs or capacity for KRAS, EGFR, ALK, etc. | Testing limited to private labs or funded projects; no reimbursement. | Select biomarkers (e.g., EGFR) available in cities; partial coverage exists. | Routine biomarker use (EGFR, ALK, PD-L1) for eligible cases with regional access. | Universal biomarker integration, rapid, reimbursed, and standardized across all regions. |
| Clinical Guidelines | No national guidelines; treatment decisions vary widely by facility. | Guidelines under development or loosely adopted; low adherence. | National guidelines published; inconsistent implementation across hospitals. | Guidelines enforced through audits, training, and digital systems. | Fully integrated clinical pathways and real-time decision support tools in all institutions. |
A Cross-Cancer Framework Built on Literature, Policy Data & Expert Validation